1 changed files with 40 additions and 0 deletions
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
## Database Functionality |
||||
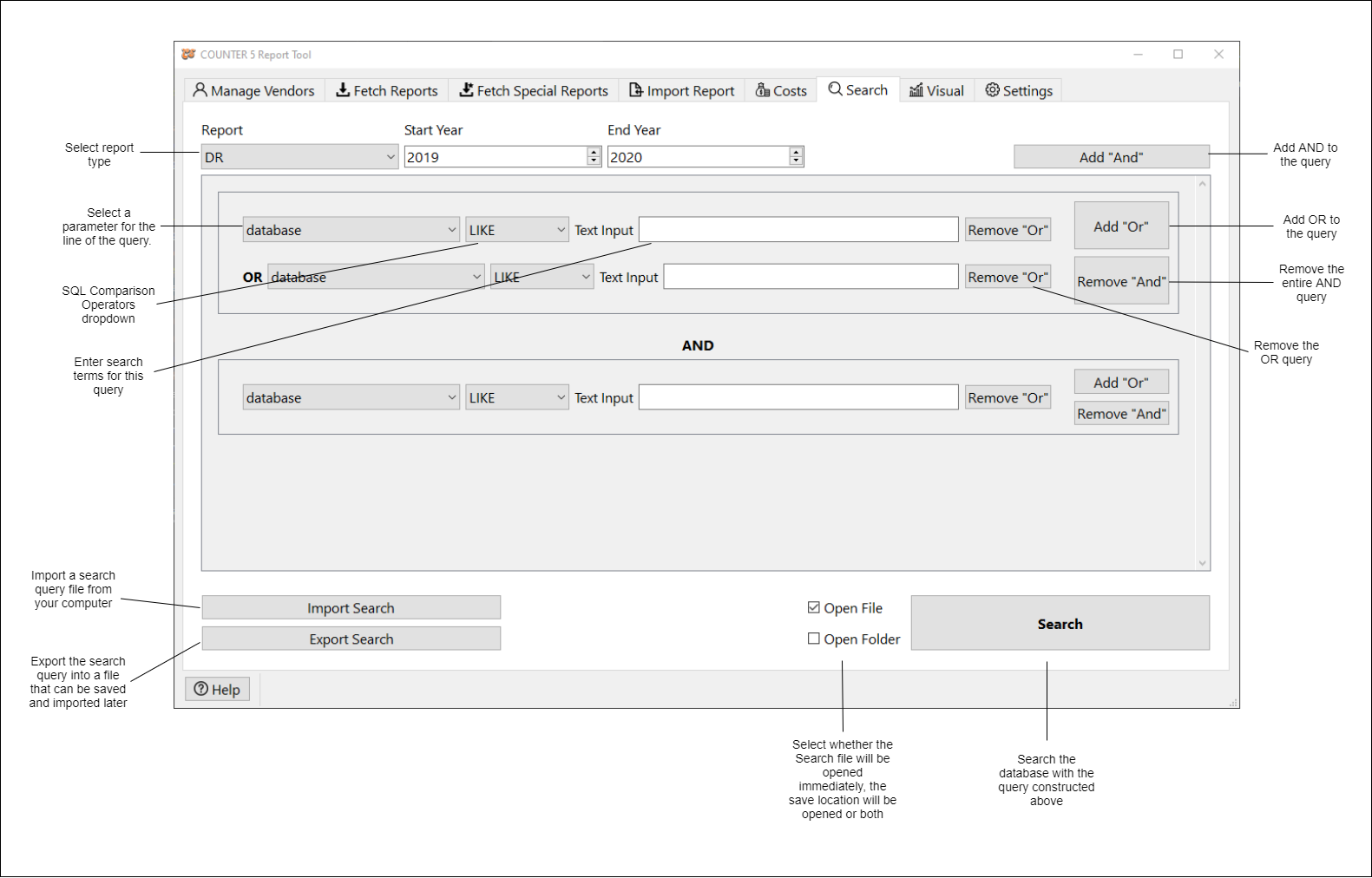
The search page is connected to an SQLite database that stores all of the report data that has been fetched. Through the interface provided you can create a query as simple or advanced as you need and it will retrieve the relevant data and return it as a TSV file. The queries in this tool are structured in Product of Sum (POS) form, which means that it is a set separated by **and** operators of sets of conditions separated by **or** operators. |
||||
|
||||
## Structuring a query |
||||
|
||||
Select a report type. |
||||
|
||||
Select a year range (start year and end year). |
||||
|
||||
For each condition you must select a **field**, **comparison operator**, and **value**. For example, choosing "database", "LIKE", and "example" would add the condition "database LIKE "example"" to the SQL query sent to the database. |
||||
|
||||
To add a condition at the **or** level, click the appropriate **Add "Or"** button. To add a set of conditions at the **and** level, click the **Add "And"** button. |
||||
|
||||
To remove a condition at the **or** level, click the appropriate **Remove "Or"** button. To remove a set of conditions at the **and** level, click the appropriate **Remove "And"** button. |
||||
|
||||
You can choose whether to open the results, open the folder the results are saved in, both, or neither, by selecting the appropriate radio button. |
||||
|
||||
Once your query is configured press the **Search** button to save the data into a TSV file. |
||||
|
||||
## Saving your search |
||||
|
||||
**Export Search** lets the user export the search query currently entered into the Search screen to a JSON file. They can then re-use it later by importing it without having to re-enter the query manually. |
||||
|
||||
**Import Search** lets the user load a previously exported search into the program and run or modify it. |
||||
|
||||
## A few notes about the parameters of a condition |
||||
|
||||
The comparison operator **<>** is the "not equal to" operator. |
||||
|
||||
The **LIKE** and **\=** comparison operators have some differences; the most important are that **LIKE** supports the wildcards **\_** (a single character) and **\%** (zero or more characters), and that **LIKE** is case insensitive on the ASCII character set. The same applies for the **<>** and **NOT LIKE** comparison operators. |
||||
|
||||
The type of input allowed for a field is shown above the value parameter box. These can be **Text**, **Integer**, or **Real** (decimal values). |
||||
|
||||
The special comparison operators **IS NULL** and **IS NOT NULL** disable the value parameter. They will check if the value in the database is null (missing), which is different from being 0 or the empty string. |
||||
|
||||
## A few other tips |
||||
|
||||
If you want to do a search for a cost below a number and want to count names (databases/items/platforms/titles) without costs entered as having zero for the cost, you have to add an **or** with the cost as the field and **is null** as the comparison operator. |
||||
Loading…
Reference in new issue